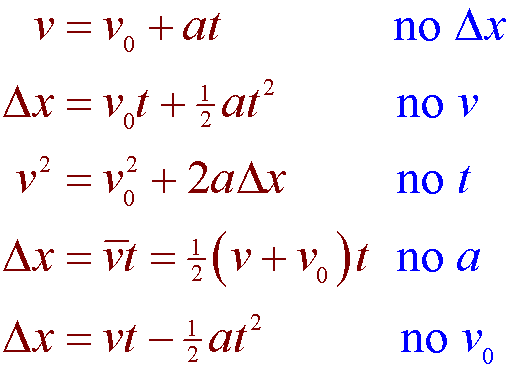Peerless Initial Velocity Formulas

Initial Velocity U 30 ms.
Initial velocity formulas. You can use this formula in various situations involving distance initial velocity final velocity and acceleration motion. Where v Velocity v 0 Initial Velocity a Acceleration t Time. Average velocity Vav 55 ms.
A motorcycle starts with an initial velocity 0 kmh 0 ms and accelerates to 120 kmh 333 ms in 5 s. Initial velocity is a movement an object has at the start of an observance period in which an acceleration starts to act on the object. Acceleration formula can be expressed in terms of initial velocity final velocity time taken or distance travelled.
Because velocity is the antiderivative of acceleration that means that v t a t and v t int a t. Initial velocity u is measured in metres per second ms acceleration α is measured in metres per second squared ms² displacement x is measured in metres m. On the other hand the final velocity is a vector quantity that measures the speed and direction of a moving body after it has reached its maximum acceleration.
Calculate its average velocity. For example given V25 a 2 t 2 solving. Position initial position initial velocity time 12 acceleration time2 The equation is written.
Linear Motion Formulas Average velocityspeed of a moving object can be calculated as v s t 1a. Where V x is the velocity along the x-axis V xo is Initial velocity along the x-axis V y is the velocity along the y-axis V yo is initial velocity along the y-axis g is the acceleration due to gravity. Velocity formula displacement time Displacement final position initial position or change in position Time taken to cover the distance.
Following are the formula of projectile motion which is also known as trajectory formula. 1 If time acceleration and final velocity are provided the initial velocity is articulated as. T is the time taken.