Impressive Oxidative Rancidity Mechanism

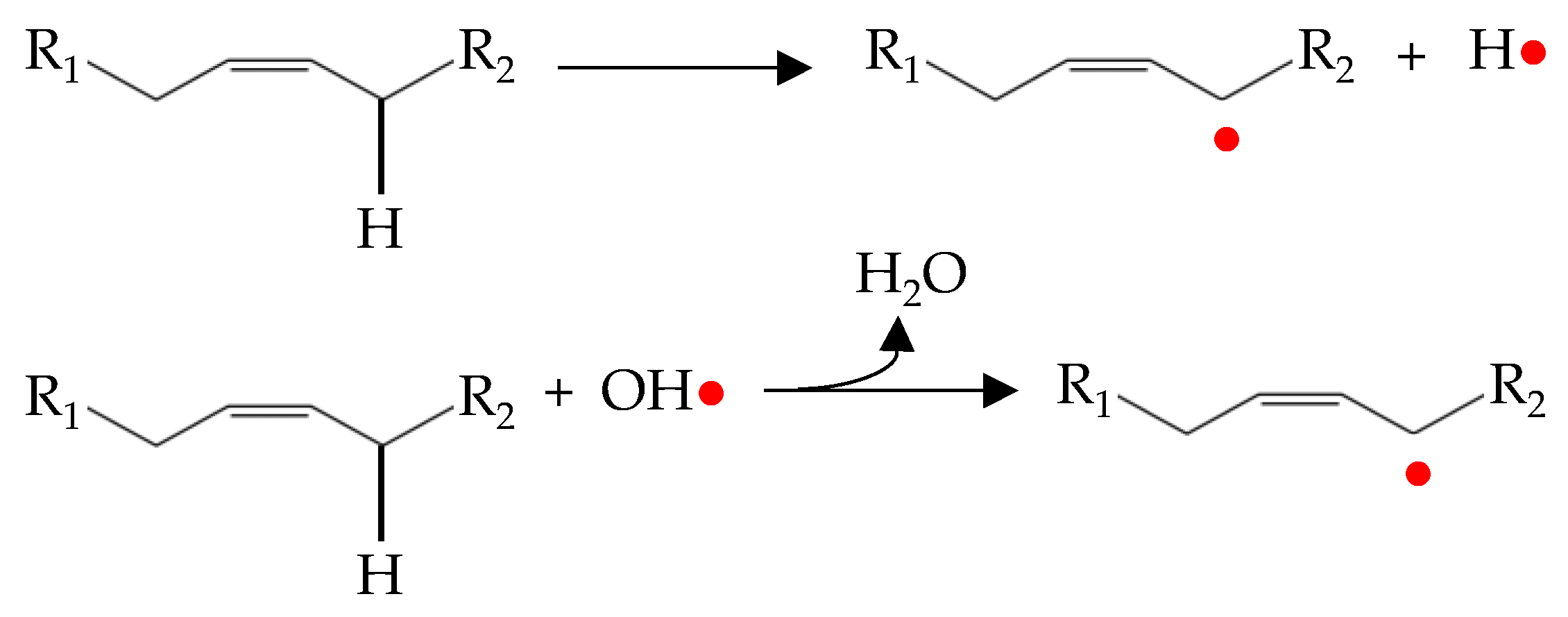
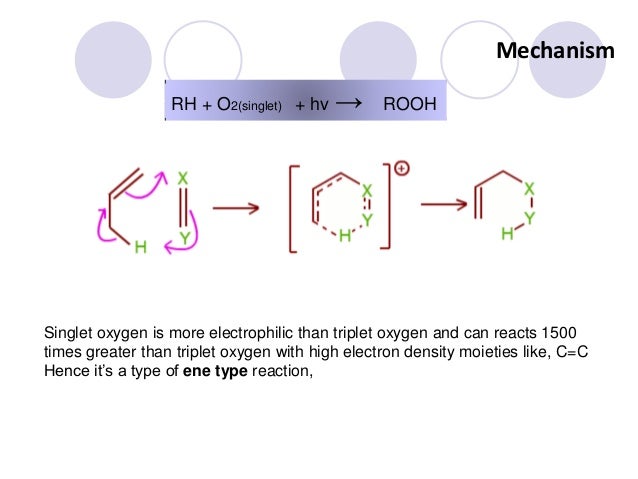
Mechanism The free radical chain reaction is sometimes referred to as the Bolland-Gee mechanism or the basic autoxidation scheme BAS and was originally based on the oxidation of rubbers but remains generally accurate for many materials.
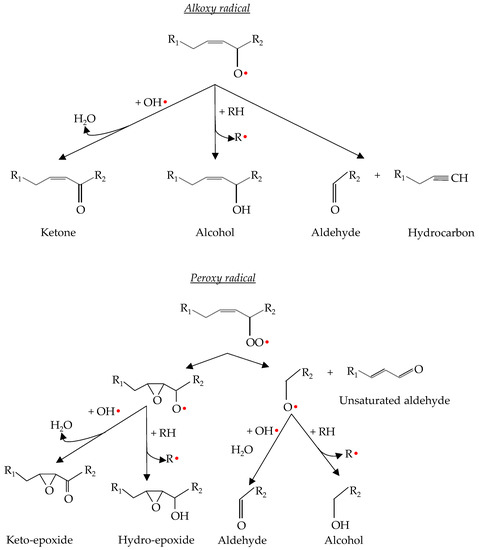
Oxidative rancidity mechanism. These chemical processes can generate highly reactive molecules in rancid foods and oils which are responsible for producing unpleasant and noxious odors and flavors. Many of these factors are obviously present during the extrusion process. But they are highly unstable toward atmospheric oxygen and start producing unpleasant smell.
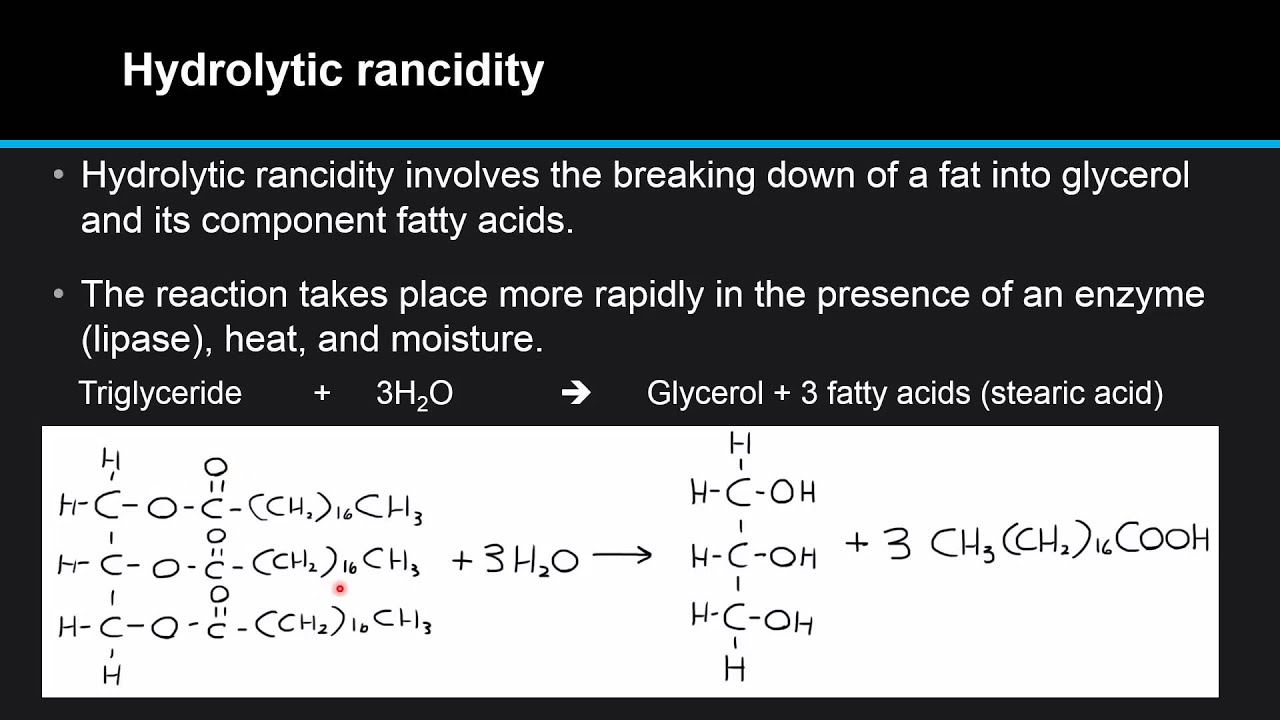
21 OXIDATION AND RANCIDITY OF FATS AND OILS Lipid oxidation is one of the major reasons that foods deteriorate and is caused by the reaction of fats and oils with molecular oxygen leading to off-flavours that are generally. Oxidative rancidity also leads to the formation of toxic compounds such as peroxides that destroy vitamins A and E in foods. Oxidative Rancidity in Fats and Oils Causes and Prevention Fats are one of the very important component of our diet.
Reaction Mechanisms free radical chain for oxidative rancidity F71 Terms in this set 10 Initiation. The various reactions that may occur are presented. The development of rancid odours and off-flavours is the most obvious change.
Oxidative rancidity is a natural process that affects fats and oil. The hydrocarbon free radicals bond with O2 to for. Rancidity is the chemical decomposition of lipids.
There are different ways by which our oils can become rancid most of them involving oxygen. Tests that measure PV and pAV are widely used to determine oxidative quality of EPADHA-containing bulk oils and finished products. Oxidation of lipids is a major cause of deterioration in the quality of lipids dairy meat and meat products and affects many characteristics such as flavor color texture and nutritive value.
The natural oil structure is interrupted and damaged by oxygen molecules in a way that can change its color odor and taste. It can be divided into. LIPID OXIDATION - TYPES MECHANISM FACTORS.