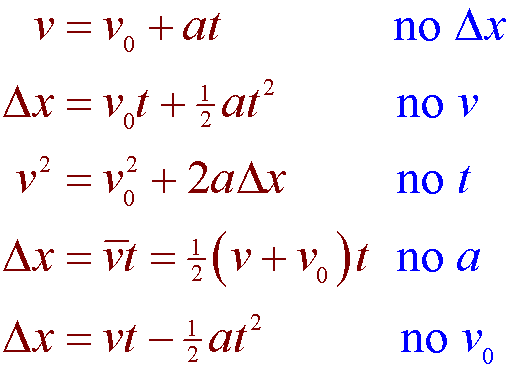Unbelievable Physics Formulas Kinematics

Physics Formulas Kinematics With Appropriate Graphs Kinematics in physics is about the motion of a body or an obeject.
Physics formulas kinematics. SAT Subject Physics Formula Reference Kinematics continued v2 f v 2 i 2ax v f finalvelocity v i initialvelocity a acceleration x displacement Use this formula when you dont havet. These are the variables physicists play around in this topic. Lecture 4 Pg 1 Kinematics Dynamics Physics 101.
W mg W weight m mass g. Kinematics Derivations cont 2 1 v f v 0 at t v f v 0a Dx v 0t at2 Dx v 0 v f v 0a av f v 0a2 v f 2 v 0 2 2aDx 2 1 Note that the top equation is solved for t and that expression for t is substituted twice in red into the Dx equation. View EPHYSICS Formulasdocx from PHYSICS --- at University of the Philippines Diliman.
Kinematic Equations for Linear Motion For constant acceleration ONLY To select the appropriate equation to solve a particular problem. Instead of differentiating velocity to find acceleration integrate acceleration to find velocity. It does not take the reference of causes of the motion ie forces etc.
EPHYSICS FORMULAS KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION X Xf Xi Displacement Average Velocity Average. Academic team of Entrancei prepared short notes and all important physics formula and bullet points of chapter Kinematics class-11 Physics. Selected PHY11 Problems with solution Quiz 1 10 November 2018 questions Physics 1 and 2 formulas Experiment 201 Appendices Exam 2017 questions and answers Physics Lab report Other related documents E101 - Laboratory Report 1 E102 - Laboratory Report 2 Friction - PHYS101L Exp110 - laboratory report EXP101 - Nice E109- Analysis.
Kinematics v ave x t v. And the terms associated with kinematics are displacement speed velocity and acceleration. You should work out the algebra to.
In such an instance as this the unknown parameters can be determined using physics principles and mathematical equations the kinematic equations. In x direction the Kinematics formulas is articulated as. Why is the time interval now written as t If we know three of these five kinematic variables for an object under constant acceleration we can use a kinematic formula see below to solve for one of the unknown variables.