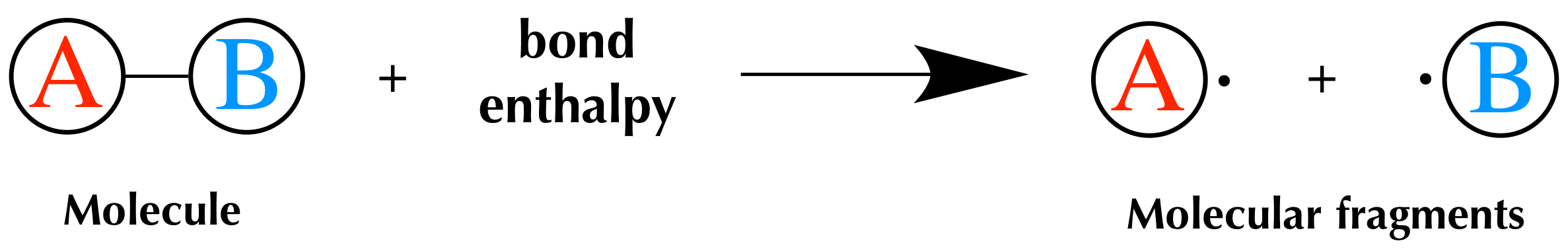Cool Bond Energies Formula
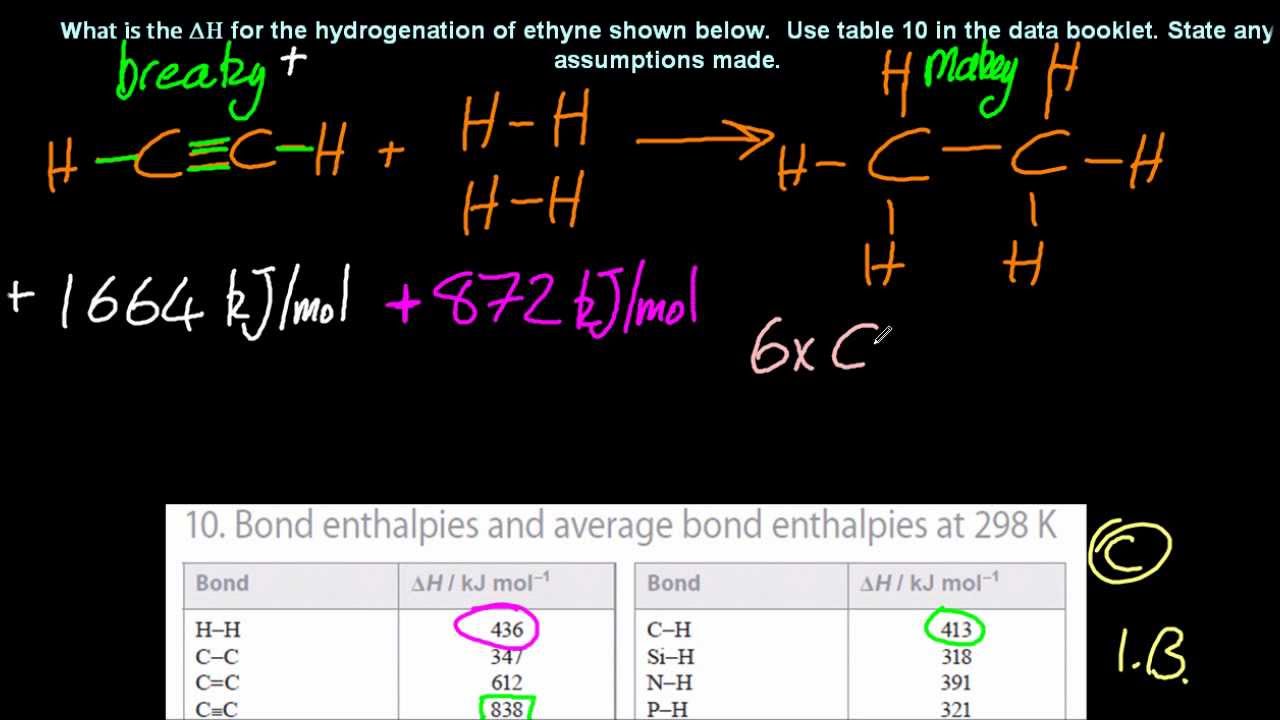
This chemistry video tutorial explains how to calculate the enthalpy of reaction by using the average bond dissociation energies listed in a table.
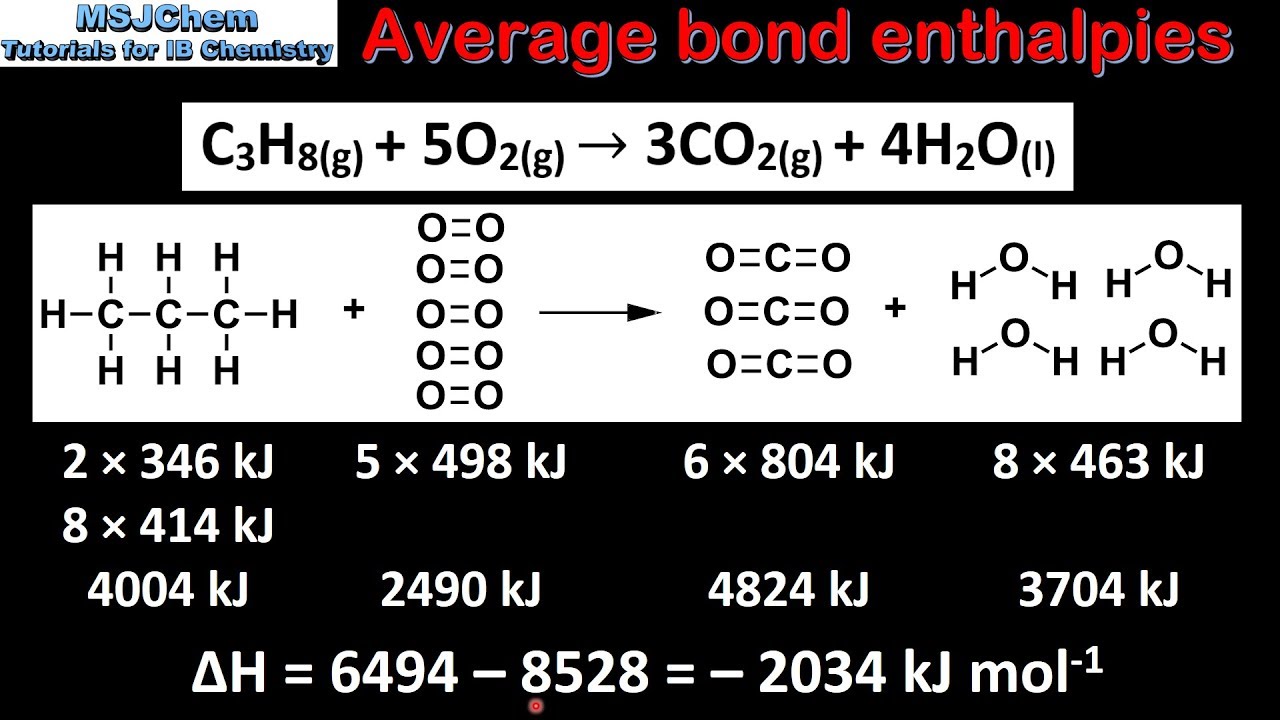
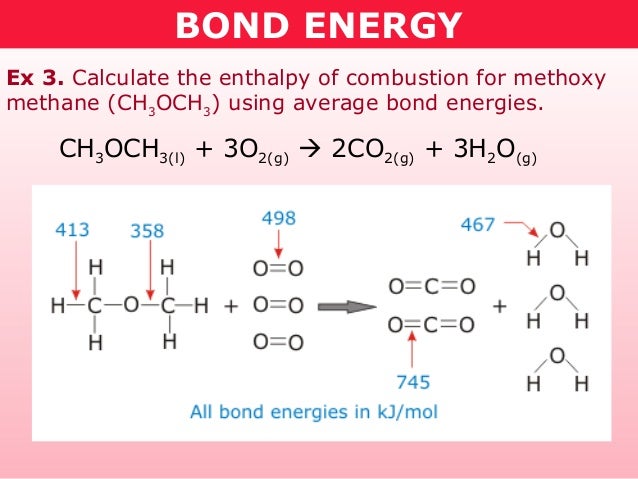
Bond energies formula. All hydrocarbons are attacked by oxygen at elevated temperatures and if oxygen is in excess complete combustion occurs to carbon dioxide and water. To calculate bond energy Add. The concept of average bond energy is used instead of the bond energy because each bond energy differs according to the type of compound and its physical state.
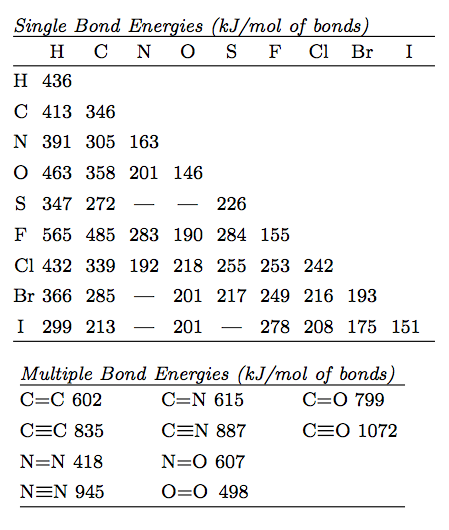
That means that many bond enthalpies are actually quoted as mean or average bond enthalpies although it might not actually say so. List the types of bonds broken in RDX along with the bond energy required to break each type. As halogen atom is more electronegative the bonded pair is more attracted towards X atom and thereby polarity develop.
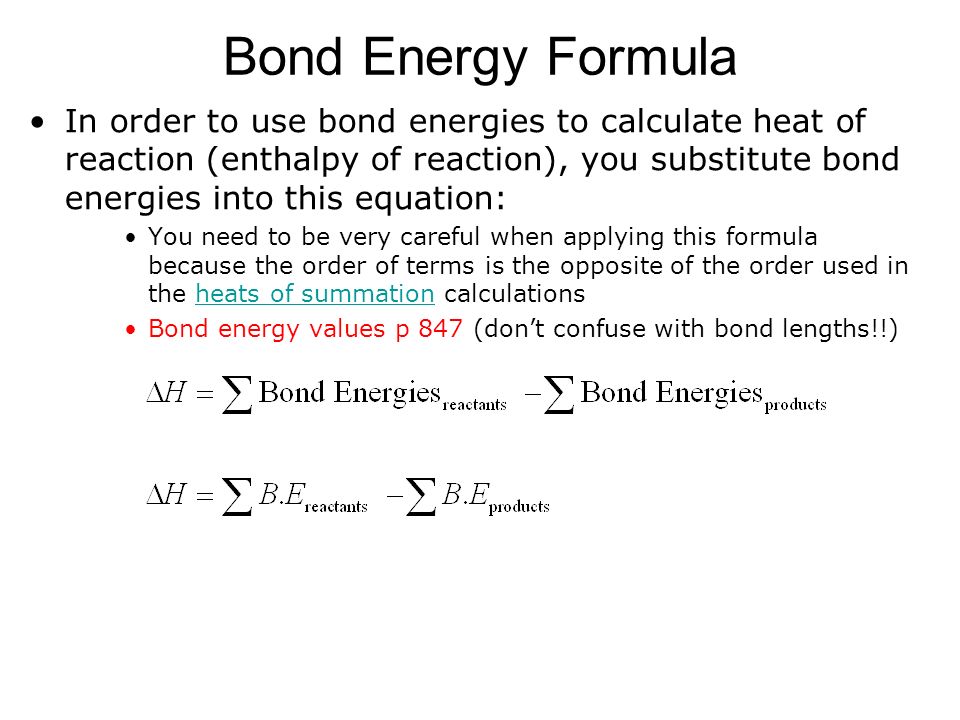
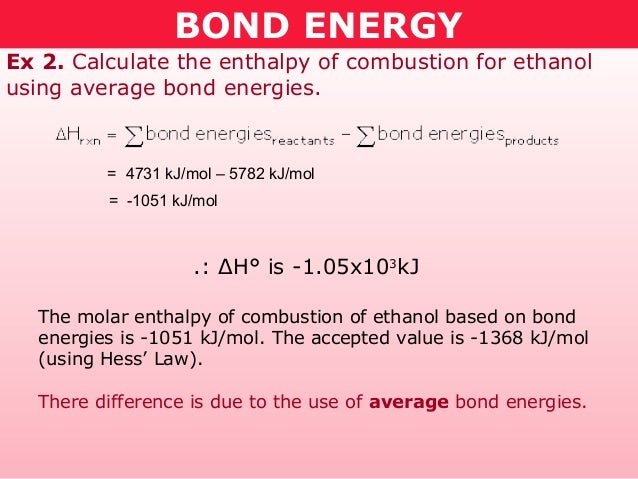
Sum of bond energies of reactants Sum of bond energies of products then H 0 in other words reaction is exothermic. The bond energy of a chemical bond in a compound is the average value of all the bond dissociation energies of that bond in the compound. They can be determined experimentally.
Atoms bond together to form compounds because in doing so they attain lower energies than they possess as individual atoms. The average bond energy is therefore 16624 kJ which is 4155 kJ per mole of bonds. When we look up the single bond energies for the H-H and Cl-Cl bonds we find them to be 436 kJmol and 243 kJmol therefore for the first step of the reaction ΔH1 436 kJ 243 kJ 679 kJ Bond breaking requires energy so we expect the value for ΔH to be positive for this step.
You can calculate the energy change in a reaction using average bond energies. 052 - Bond Length and Bond EnergyIn this video Paul Andersen explains how the bond length and bond energy are calculated using an energy distance graph. A CC bond has an approximate bond energy of 80 kcalmol while a CC has a bond energy of about 145 kcalmol.
Well need some basic math for this section. A quantity of energy equal to the difference between the energies of the bonded atoms and the energies of the separated atoms is released usually as heat. This give rise to additional attractive force for binding.